

This will be graded along with the rest of your codebase at the course Milestone 1.
The idea of the final project part before Milestone 1 is to create an interface-implementation separation. Why?
TimeSeries with its list based implementation as a base class.So let us get to it! Take a look at the inheritance diagram below.
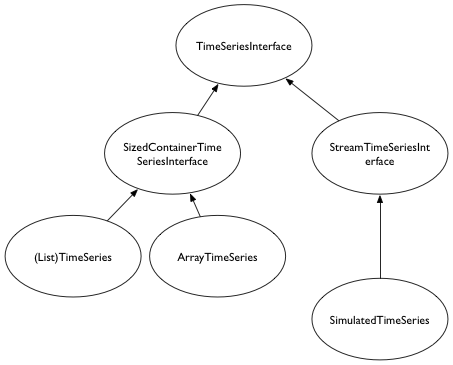
TimeSeriesInterface ABCThis should be a well documented ABC which defines a set of common methods that might be used both in sized-container based time series as well as stream based and simulated time series (for e.g. the time series range(1000) or that represented by successive (to infinity) fibonaccis).
I'll let you decide what methods ought to go into this ABC and what dont, but can tell you that the constructor is not part of the interface, and that the way to think about this is: that for example, __iter__ makes sense both for containers and iterables, but that values only makes sense for containers. Or in other words, iterators make sense here, but not containers.
So the way to think about it is: which methods you defined in the last installation of the project so far ought to be hoisted into the common interface?
SizedContainerTimeSeriesInterface ABCThis is also an ABC, but its one that inherits from the TimeSeriesInterface ABC.
This ABC now adds in the methods you left out in the TimeSeriesInterface which pertain to its "containerness": the notions of indexing, length, and returning arrays in addition to iterators
So now the existing TimeSeries and ArrayTimeSeries must be reparented. Note that some methods in ArrayTimeSeries might have been inherited from Timeseries. Some of this code may have to be defined in one of the above ABC's (its perfectly fine for ABCs to not have all methods @abstractmethoded)
Make sure that all tests you had working earlier still work. These tests will ensure that this refactoring effort on your part does not break anything.
Note that you'll have different constructors here: thats ok. The constructors are not (yet) part of any common interface.
StreamTimeSeriesInterface and a SimulatedTimeSeries class that inherits from it.Ok, so now its time to handle those time-series which dont have an underlying array (or more generally, storage). At least two types of time series fall into this category:
To handle these cases, we'll add a single additional abstract (generator) method to the StreamTimeSeriesInterface:
def produce(self, chunk=1):
pass
which produces a chunk sized bunch of new elements into the timeseries whenever it is called (document it).
Now create a SimulatedTimeSeries class which has a constructor that takes a generator as an argument, starts it, and perhaps primes it. (or uses a boolean to keep track of the priming)
An example of such a generator would be make_data from hw6.
The subtlety here is that the produce method can handle data in chunks, so to implement this class properly, the instance variable used by the constructor that saves the called generator function can be used inside produce to advance by chunk nexts.
Indeed you could use make_data to test your code.
Add mean and std method interfaces at the appropriate places in the hierarchy. These methods should return floating point numbers. (an optional chunk argument is needed in some cases) Also add an online_mean and online_std for StreamTimeSeriesInterface time-series, which themselves return the appropriate time-series. These "online" methods should return new SimulatedTimeSeries of the appropriate type, and when produce is called on them, should produce chunk means and standard deviations, starting from the current state of the time series. (notice that this will be the meaning of mean and std with non default chunk as well: ie, the last chunk observations' statistic )
Put this code into your project repo.